

medical-conditions/blood-heart-circulation/atrial-flutter/treatments.html Atrial flutter versus atrial fibrillation in a general population: Differences in comorbidities associated with their respective onset.
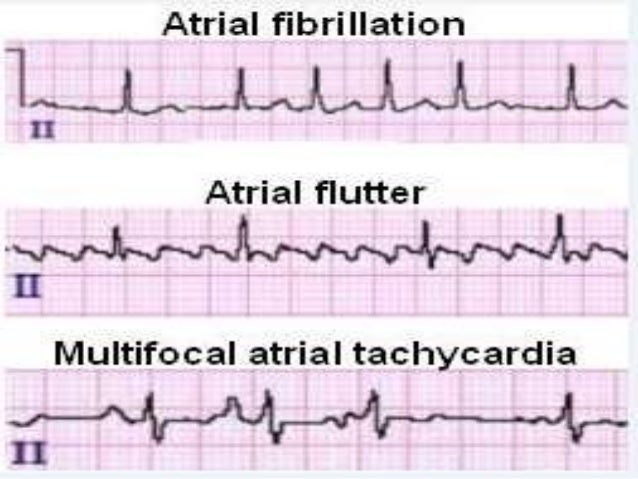
This abnormal heart rhythm may cause blood to pool in the atria and form clots. During atrial fibrillation, the heart’s two upper chambers, called atria, beat rapidly, chaotically, and out of sync with the two lower chambers, or ventricles.
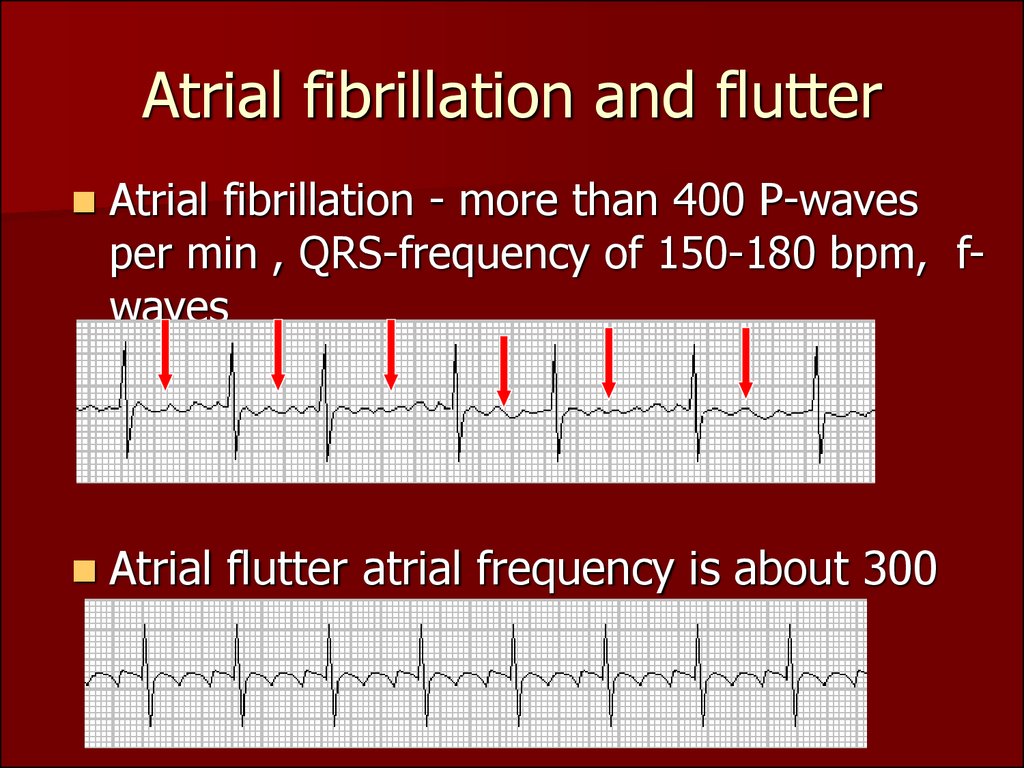
(Usually, the heart beats 60 to 150 times a minute. diseases-conditions/atrial-fibrillation/diagnosis-treatment/treatment/txc-20164944 Symptoms often include heart palpitations, shortness of breath and weakness. Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, is an unusually fast heartbeat in the heart’s upper chambers, sometimes as many as 400 beats or more a minute.

nottingham.ac.uk/nursing/practice/resources/cardiology/fibrillation/atrial_flutter.php Cardiology teaching package: Atrial flutter.Obstructive sleep apnea in patients with typical atrial flutter: Prevalence and impact on arrhythmia control outcome. Patient-Resources/Heart-Diseases-Disorders/Atrial-Flutter You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. Still, ablation therapy is typically only used when medications can’t control the conditions. However, ablation is usually considered the best treatment for atrial flutter. Medication is usually the first treatment for AFib. The surgeon makes small cuts or burns in the heart’s atria. Maze surgery: Maze surgery is an open-heart surgery. After this type of ablation, you’ll need a pacemaker to maintain a regular rhythm. The AV node connects the atria and ventricles. NOACs include dabigatran (Pradaxa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis) and edoxaban (Savaysa).Įlectrical cardioversion: This procedure uses an electrical shock to reset the rhythm of your heart.Ĭatheter ablation: Catheter ablation uses radiofrequency energy to destroy the area inside your heart that’s causing the abnormal heart rhythm.Ītrioventricular (AV) node ablation: This procedure uses radio waves to destroy the AV node. NOACs are now recommended over warfarin unless the person has moderate to severe mitral stenosis or has an artificial heart valve. blood-thinning medications such as non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants (NOACs) or warfarin (Coumadin) to prevent stroke or heart attack.amiodarone, propafenone, and flecainide to convert the rhythm back to normal.It can cause many of the same symptoms as atrial fibrillation, and in fact, roughly 30 percent of. calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers to regulate the heart rate In atrial flutter, the hearts rhythm is rapid but regular.Treatment for both conditions may involve: People are also more likely to develop tachycardia as they age or if they have a family history of the condition.Treatment for AFib and atrial flutter has the same goals: Restore the normal rhythm of the heart and prevent blood clots. Factors that contribute to electrical system problems include:Ĭonditions that can strain the heart increase the likelihood of developing tachycardia. Tachycardia can be caused by factors that disrupt the electrical impulses of the heart. Ventricular fibrillation (VF) - ventricles fail to pump blood at all during rapid rhythm.Ventricular tachycardia (VT) - a ventricular electrical abnormality where the ventricles poorly fill with blood.Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) or paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) - Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is the leading cause of SVT in children or young adults.Atrial flutter - an arrhythmia similar to atrial fibrillation yet less serious.Atrial fibrillation (AFib or AF) - irregular heartbeat associated with heart disease, overactive thyroid or alcoholism.Sinus tachycardia - often the body’s normal response to situations such as stress, anxiety or distress can be caused by conditions such as anemia, low blood pressure or thyroid disease.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
